Lysosomal Gene Expression
Western blot analysis comparing protein expression in iPSC-derived cortical and dopaminergic neurons across five conditions (control, IFN-γ, PFF, and combined PFF+IFN-γ). The data show that dopaminergic neurons undergo pronounced downregulation of key lysosomal and stress-response proteins, including LAMP1, LAMP2, TFEB, and NRF2, following the dual-hit treatment. In contrast, cortical neurons displayed relatively stable expression of these proteins. At baseline, cortical neurons expressed higher levels of lysosomal proteins and TFEB than dopaminergic neurons, suggesting intrinsic resilience to lysosomal stress .

Lysosomal Damage
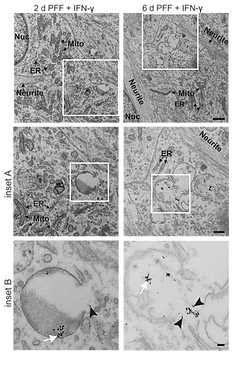
In this experiment, researchers asked whether lysosomes are damaged during the buildup of α-synuclein inclusions. They used galectin-3, a protein that naturally binds to sugars exposed on ruptured lysosomal membranes, as a reporter for damage. Dopaminergic neurons were treated with α-synuclein fibrils and an immune signal, and then stained for galectin-3 alongside the lysosomal marker LAMP1. Under these conditions, galectin-3 formed bright puncta on lysosomes, showing that their membranes had been breached. Electron microscopy confirmed this result by capturing fibrils inside broken lysosomes and leaking into the cytosol, linking lysosomal rupture directly to inclusion formation.

Lysosomal Isolation
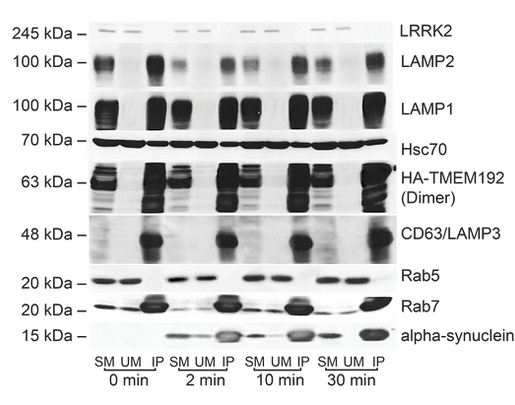
Lysosomes were purified from cells expressing HA-tagged TMEM192-RFP using HA-magnetic bead immunoprecipitation. Western blot analysis of the immunoprecipitated fraction confirmed strong enrichment of lysosomal markers including LAMP1, LAMP2, and Rab7, while early endosome and cytosolic markers (Rab5 and LRRK2) were absent. CD63/LAMP3, a marker of lysosomes and multivesicular bodies, was most highly enriched. Fluorescently labeled α-synuclein fibrils (PFFs) were also detected in the lysosome fraction as early as 2 minutes after uptake, demonstrating their rapid transport to lysosomes

Live-Imaging: Lysosomal pH
Lysosomal integrity was assessed using LysoSensor and LysoTracker staining in dopaminergic neurons under different treatment conditions. Neurons treated with IFN-γ or with the dual-hit paradigm (PFF+IFN-γ) showed lysosomes with higher pH values (measured by LysoSensor) compared to control and PFF-only groups, indicating impaired acidification. Complementary LysoTracker staining revealed a marked reduction in the number of lysosome-positive puncta in IFN-γ– and dual-hit–treated neurons, further confirming disrupted lysosomal function