Co-culturing for Direct Comparison of Genetic Knockdown
Comparing CHC knockdown and control cells side-by-side
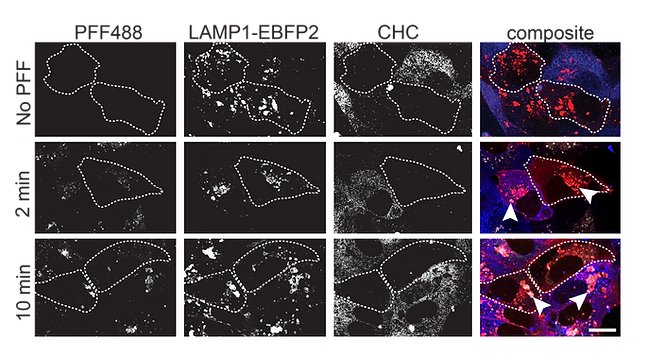
To directly compare conditions, we co-cultured control siRNA–treated cells and CHC siRNA–treated cells together in the same well, creating a mosaic of knockdown and non-knockdown populations. After PFF exposure, this setup allowed us to assess uptake side by side under identical conditions. Notably, PFF internalization was indistinguishable between the two populations, demonstrating that uptake occurs independently of clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
Co-culturing of Stable Cell Lines
CD63-GFP (Donor Cells) were incubated with PFF633 for 24 hrs. They were then trypsinized and co-plated with CD9-RFP cells that have not been exposed to PFF.
Experimental Design:
To track the transfer of pathogenic material between cells, we co-cultured U2OS donor cells stably expressing CD63-GFP that had been exposed to PFFs or vehicle control with acceptor cells expressing CD9-mCherry. After extensive washing and replating, donor and acceptor cells were incubated together for 12 or 24 hours. At both time points, we detected PFFs (blue) and CD63 (green) within CD9-positive acceptor cells (red), indicating intercellular transfer. Insets highlight compartments in acceptor cells that contained both CD63 and PFF, pointing to exosome-mediated propagation of fibrils.

Result: PFF633 and CD63 colocalize in Acceptor cells (see arrows).