CRISPR Gene Editing
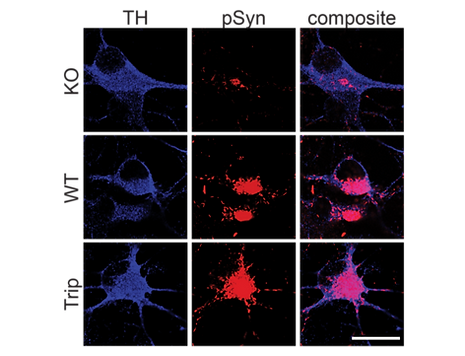
To dissect genetic contributions to Parkinson’s pathology, we generated iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons lacking α-synuclein or GBA (below). GBA knockout heightened vulnerability to fibril-induced inclusions, whereas α-synuclein knockout abolished pathology entirely. These results established causal links between genetic risk, lysosomal dysfunction, and Lewy body pathology.

Generation of GBA-KO
-
(A) Sequence alignment of the parental iPSC line (AIW002-02) with the edited GBA-KO line.
-
(B) PCR analysis showed a shift from the wild-type 739 bp fragment to a 641 bp product in the GBA-KO line.
-
(C) Western blotting confirmed complete loss of GBA protein across iPSCs, NPCs, and differentiated dopaminergic neurons.
-
(D) G-banding demonstrated that the GBA-KO iPSCs maintained a normal karyotype.
-
(E) Immunocytochemistry of GBA-KO iPSCs shows robust expression of pluripotency markers.
α-synuclein KOs generated from SNCA triplication patient
Isogenic iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons from an SNCA triplication line were edited to create wild-type and knockout controls, then treated with PFFs and IFN-γ to assess the role of endogenous α-syn.